Retinal Surgery
Retinal surgery is a type of eye surgery that focuses on the retina, the thin layer of tissue located at the back of the eye responsible for converting light into impulses that travel from the optic nerve to the brain, enabling vision. Retinal surgery is typically performed to repair or treat various retinal conditions and diseases that can affect vision.
Causes for Retinal surgery:
- Retinal Detachment : When the retina separates from the layers of the eye underneath it, this happens. In order to repair the retina and avoid irreversible vision loss, surgery is frequently required.
- Macular Holes : These are small breaks in the macula, the central portion of the retina responsible for sharp, central vision. Surgery may be needed to close the hole and improve vision.
- Epiretinal Membranes : Also known as macular puckers, these are thin layers of scar tissue that form on the surface of the retina, causing visual distortion. By removing the membrane, surgery can enhance eyesight.
- Vitreous Hemorrhage : This occurs when blood leaks into the vitreous, the gel-like substance that fills the inside of the eye, often due to conditions like diabetic retinopathy or a retinal tear. Surgery may be necessary to remove the blood and repair any underlying issues.
- Macular Degeneration : In some cases of advanced age-related macular degeneration (AMD), surgical treatments such as retinal laser therapy or injections of medications directly into the eye may be considered to slow the progression of the disease and preserve vision.
Retinal surgery can involve various techniques, including:
- Vitrectomy : A surgical procedure to remove some or all of the vitreous gel from the eye, often used in the treatment of retinal detachment or vitreous hemorrhage.
- Scleral Buckling : A surgical technique to repair a retinal detachment by placing a silicone band (buckle) around the outside of the eye to push the wall of the eye inward and relieve traction on the retina.
- Laser Photocoagulation : A procedure where a laser is used to seal or destroy abnormal blood vessels or to create tiny burns in the retina to prevent or treat retinal tears or detachments.
- Injection Therapy : Intravitreal injections of medications, such as anti-VEGF drugs or corticosteroids, directly into the eye to treat conditions like macular degeneration or diabetic retinopathy.
Retinal surgery is typically performed by ophthalmologists who specialize in diseases and surgery of the retina and vitreous. While these procedures can be highly effective in preserving or restoring vision, they also carry risks, and outcomes can vary depending on factors such as the specific condition being treated and the overall health of the eye. It's essential for individuals considering retinal surgery to discuss the potential benefits, risks, and alternatives with their eye care provider.
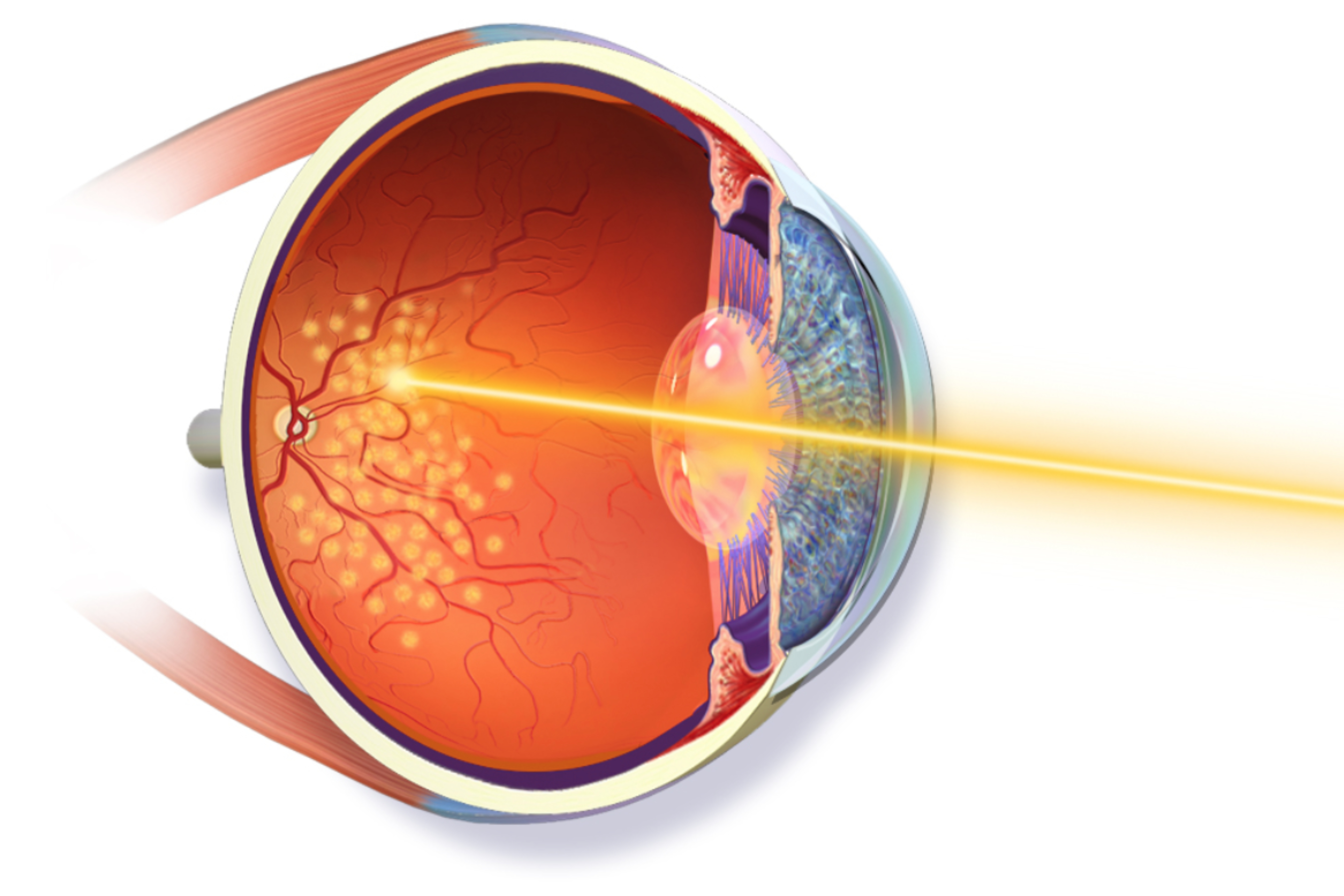
Laser treatment for Retinal surgery:
Laser treatment for retinal surgery is a common procedure used to treat various retinal conditions.
Purpose of Laser treatment for retinal surgery:
Laser treatment for retinal surgery is typically aimed at repairing or sealing damaged blood vessels in the retina, treating retinal tears or breaks, managing diabetic retinopathy, addressing macular degeneration, or treating certain types of glaucoma.
Procedure of Laser treatment:
During the procedure, the patient may receive local anesthesia, and the eye is held open with a speculum to prevent blinking. A special lens is placed on the eye to focus the laser beam precisely on the targeted area of the retina. The surgeon then uses the laser to make tiny burns or to seal blood vessels or tears in the retina.
Types of Laser Surgery:
- Photocoagulation : This entails making tiny burns on the retina with a laser. These burns seal leaking blood vessels or create scars to prevent the progression of certain retinal conditions.
- Photodynamic Therapy (PDT) : In this case, a medication that is light-sensitive is injected into the circulation and activated by laser light. It's used primarily for treating certain types of macular degeneration.
- Laser Retinopexy : This procedure is used to treat retinal tears by creating burns around the tear, which causes scarring and helps to seal the tear, preventing retinal detachment.
- Selective Laser Trabeculoplasty (SLT) : This is used to treat certain types of glaucoma by using laser energy to target specific cells in the trabecular meshwork, improving drainage of aqueous humor from the eye and reducing intraocular pressure.
Benefits of Laser surgery for retinal conditions:
Laser surgery for retinal conditions offers several benefits, including precise targeting of affected areas, minimally invasive nature, outpatient procedure in most cases, and relatively quick recovery times.
Risks and Side Effects of Laser treatment for retinal surgery:
While laser treatment for retinal surgery is generally safe, there are some potential risks and side effects, such as temporary vision changes, discomfort during the procedure, risk of infection, and in rare cases, worsening of the condition being treated.
Postoperative Care:
Patients typically need to follow postoperative instructions carefully, which may include using prescribed eye drops, avoiding strenuous activities, and attending follow-up appointments to monitor healing and assess the effectiveness of the treatment.
It's essential for individuals considering laser treatment for retinal surgery to consult with an experienced ophthalmologist or retinal specialist to determine the most appropriate treatment approach based on their specific condition and medical history.
- Cataract Surgery & Treatment
- Multifocal Intraocular Lens (IOL)
- ICL (Implantable Collamer Lens)
- Glaucoma Surgery & Treatment
- Eye Trauma Care
- Oculoplastic, Squint, Ptosis
- Computerized Eye Testing
- Contact Lens Clinic
- Lasik Surgery
- Refractive Surgical Corrections
- Diabetic Retinopathy Screening & Treatment
- Retinal Surgery / Laser Treatment
