Eye Trauma Care
Sports injuries, collisions, and foreign objects in the eye can all cause eye injuries. Pain, edema, redness, and other symptoms may result from them. Some experience alterations in their vision or light flashes. Severe eye trauma may result in irreversible visual loss.
Eye injuries include bruises, punctures, and scratches. They may arise from ocular trauma, chemical exposure, or foreign objects in the eye.
If you have had an eye injury, consult an ophthalmologist straight once. Rest and home remedies can help certain eye ailments recover. Others may result in severe vision loss and damage to the eyes.
What are the most common Eye injuries?
-
Eye injuries range from mild to severe. Few types of Eye injuries include:
- Black eye : A black eye is the result of trauma to the eye or the surrounding tissue. The area around the eye is bruised, swollen and painful. The eyelid may also be cut. The swelling can interfere with vision.
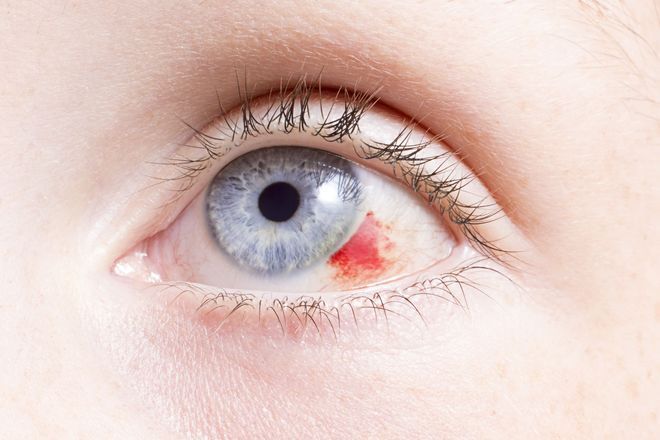
- Bleeding in the eye : An eye surface hemorrhage (bleeding) can result from straining too hard (such as during a cough) or from trauma to the eye. A sub conjunctival hemorrhage happens when blood appears in the clear skin part of the eye (the conjunctiva) that covers the white part (the sclera). Additionally, blood can collect between the iris and cornea, or the colorful portion of the eye and its transparent clear cornea. This bleeding is called Hyphemia.
- Burns and irritation : Vision loss can result from burns, irritations, and other substances that harm or burn the eyes.
- Corneal abrasion : The cornea can be scratched by foreign objects, nails, contact lenses, and other things. The clear, translucent region in front of the eye is called the cornea. Corneal abrasions result in discomfort, light sensitivity, and moisture of the eyes.
- Injury from a foreign object : Vision issues and eye discomfort can arise from foreign bodies lodged in the eye. The most common foreign objects in the eye include dirt or debris, sawdust or shattered glass. Contact lenses can cause eye injuries when they stay in the eye too long.
- Orbital (eye socket) fractures : A fracture can result from trauma or blunt force to the surrounding bones of the eye. Usually, orbital fractures occur when a fist or other object strikes the eye. The eye socket's internal bones break apart in an orbital blowout fracture. The muscles that hold up the eyes may rip, strain, or get stuck. Children are especially susceptible to this.
- Retinal detachment : A detached retina may result in irreversible visual loss. It generally happens as a result of changes brought on by aging or ocular damage. It occurs when the retina, which is a thin layer of tissue on the back of the eye, separates from the eye wall.
What are the symptoms of eye injuries?
Symptoms vary based on the type of injury. They may appear suddenly or develop over time.
Signs of an eye injury include :
- Pain and swelling : Particularly when you try to open, close, or move your eye, it might hurt. It's possible that the eye is touch-sensitive. Swelling can affect the eyeball, eyelid or entire face.
- Bruising and redness : Any area of the eye might seem bruised or red.
- Vision changes : It's possible to observe bursts of light or floating black dots. You can experience additional vision issues, such as double or hazy vision, in addition to eye floaters.
- Problems with eye movement : It could be difficult for you to move your eyes. It is possible for one eye to shift apart from the other.
- Changes in eye appearance : A crossed eye might be the result of strabismus. The pupils might have irregular sizes or extremely big or tiny diameters. One eye may appear sunken or protrude more than the other from the eye socket.
- Bleeding : The white part of the eye may look bright red, or you might see small red or black spots in the eye. An eye injury may be indicated by a red eye
What causes eye injuries?
The majority of eye injuries result in harm to the surrounding tissues and bones as well as the eye itself.
When using saws or drills, or when edging or mowing the grass, eye injuries might occur. Among the other frequent reasons for eye injury are:
- Sports : Injuries can occur from flying baseballs, tennis balls or volleyballs. Eye injuries can also result from contact sports (e.g., elbow to the face during a basketball game).
- Accidents : Eye injuries can result from a variety of mishaps, such as falls, trauma from sharp objects, and blunt force injuries. Eye injuries from collisions or broken glass are frequently the result of car accidents. Grease splatters from cooking or chemicals used in house cleaning might cause eye injury.
- Workplace hazards : It is more common for those who deal with chemicals, lasers, and other irritants to have eye injuries at work.
- Strain : Eye bleeding can occur from severe Eye exertion while coughing, vomiting, or carrying heavy objects.
What are the treatments for eye injuries?
If you or your child has an eye injury, call for help right away. The kind and extent of the eye damage determine the course of treatment. Serious injuries may require surgery.
For minor eye injuries, treatment may include:
- Cold compresses : Icepacks ease pain and minimize swelling.
- Eye flushing : Use clean water to flush chemicals and other irritants for approximately fifteen minutes.
- Eyedrops : To aid in the healing of your eye, your doctor could recommend eyedrops.
- Eye patch : You may give your eye some rest while it heals by covering it.
Can I prevent eye injuries?
Planning ahead and using the appropriate gear can help prevent the majority of eye injuries. To prevent harm to your eyes, you ought to:
- Wear protective glasses or goggles : Put on safety goggles or glasses: Activities that increase your risk of eye damage, including sports, call for the extra precaution of wearing eye protection. When utilizing chemicals, power tools, cutting wood, or performing yard labor, use the proper eye protection.
- Store chemicals safely : Keep bleach, cleansers, detergents, and other chemicals out of children's reach. Protect your eyes when using cleaning products.
- Be careful with fireworks : Only adults should handle fireworks. Read labels carefully, and always wear eye protection.
- Never play with laser pointers : Never point a laser pointer in someone else's direction or allow your kids to play with one.
Eye trauma care involves the assessment, treatment, and management of injuries or damage to the eye. It requires prompt evaluation and intervention to prevent vision loss or other complications.
Key aspects of Eye Trauma Care:
- Initial Assessment :
- Assess the extent of the injury, including whether it involves the eyelids, conjunctiva (the clear membrane covering the white part of the eye), cornea, or other structures.
- Evaluate visual acuity and pupil reactions.
- Check for signs of orbital fractures or foreign bodies.
- Immediate First Aid :
- Rinse the eye with clean water or saline solution if there's chemical exposure or foreign material in the eye. Avoid rubbing the eye, as it can cause further damage.
- Cover the injured eye with a protective shield or clean, soft material to prevent further trauma.
- Seek Medical Attention :
- Eye trauma often requires evaluation by an ophthalmologist or an eye care professional. If the injury is severe or vision is affected, seek medical attention immediately.
- Do not attempt to remove any embedded foreign objects; leave this to a healthcare professional.
- Treatment :
- The kind and degree of the injury determine the course of treatment. It may include medications, such as antibiotics to prevent infection or pain relievers for discomfort.
- Surgical intervention may be necessary for severe injuries, such as repairing a ruptured globe or removing foreign bodies.
- In cases of chemical exposure, irrigation with copious amounts of water is crucial to flush out the chemical and minimize damage.
- Follow-Up Care :
- Regular follow-up visits may be necessary to monitor healing and address any complications.
- Compliance with medication regimens and activity restrictions is essential for optimal recovery.
- Prevention :
- Educate individuals about the importance of eye protection during activities with potential eye hazards, such as sports, construction work, or home repairs.
- Use appropriate protective eyewear, such as goggles or safety glasses, to minimize the risk of eye injuries.
- Psychological Support :
- Eye trauma can be distressing for patients, potentially leading to anxiety or depression. Offering psychological support and counseling may be beneficial for coping with the emotional impact of the injury.
- Rehabilitation :
- In cases where vision loss or impairment occurs, rehabilitation services, such as vision therapy or low vision aids, may be helpful in maximizing remaining vision and adapting to any changes in visual function.
Prompt and appropriate management of eye trauma is crucial for optimizing outcomes and minimizing the risk of complications, including permanent vision loss.
- Cataract Surgery & Treatment
- Multifocal Intraocular Lens (IOL)
- ICL (Implantable Collamer Lens)
- Glaucoma Surgery & Treatment
- Eye Trauma Care
- Oculoplastic, Squint, Ptosis
- Computerized Eye Testing
- Contact Lens Clinic
- Lasik Surgery
- Refractive Surgical Corrections
- Diabetic Retinopathy Screening & Treatment
- Retinal Surgery / Laser Treatment
