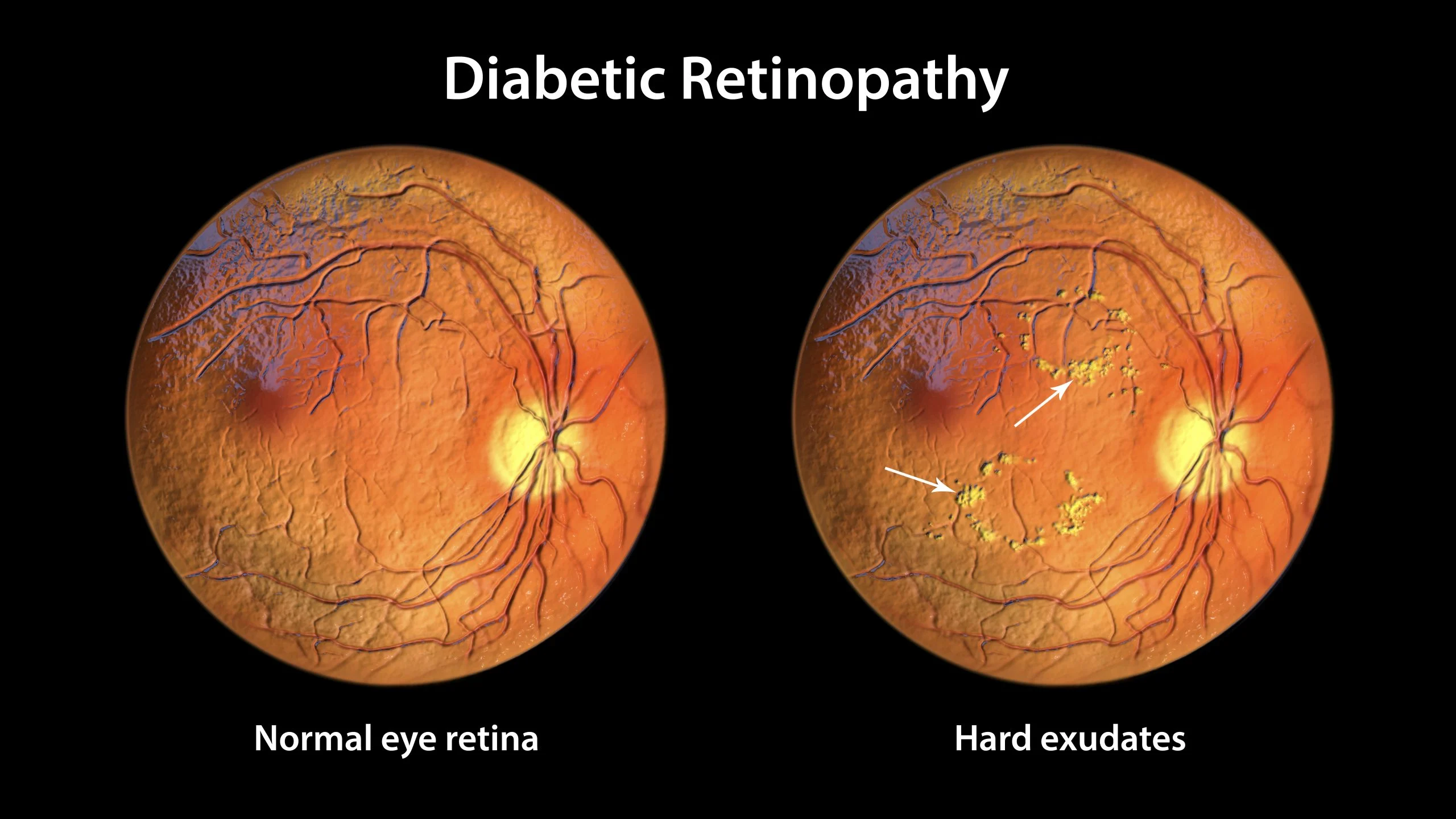
Diabetic Retinopathy Screening & Treatment
The retina is impacted by the eye condition known as diabetes-related retinopathy. Damage to the blood vessels in the retina, the light-sensitive tissue in the back of the eye, is the cause of it. If diabetic retinopathy is not treated, it may result in blindness or vision impairment.
Symptoms of Diabetic Retinopathy
Since diabetic retinopathy normally doesn't show symptoms until it's more advanced, you won't often notice it in the early stages. Nevertheless, during diabetic eye screening, photos of the eyes can be used to detect early indicators of the illness.
See your physician or the diabetic care team right away if you encounter:
- gradually worsening vision
- sudden vision loss
- shapes floating in your field of vision (floaters)
- blurred or patchy vision
- eye pain or redness
- difficulty seeing in the dark
Even though you may not have diabetic retinopathy based only on these symptoms, it's nevertheless crucial to have your eyes examined. Don't hold off till your subsequent screening session.
Screening and treatment of Diabetic Retinopathy:
Screening of Diabetic Retinopathy:
- Regular Eye Exams : People with diabetes should have regular eye exams, at least once a year, to check for diabetic retinopathy and other eye problems.
- Dilated Eye Exam : During a dilated eye exam, drops are placed in your eyes to widen or dilate the pupils. This makes it possible for the eye doctor to examine more of the interior of your eyes and look for any indications of the illness.
- Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT) : This non-invasive imaging test uses light waves to take cross-section pictures of your retina, allowing your doctor to see if fluid or blood vessels are leaking into your retina.
- Fluorescein Angiography : In this test, a special dye is injected into your arm and pictures are taken as the dye passes through the blood vessels in your retina. It helps identify leaking blood vessels.
Treatment of Diabetic Retinopathy:
- Early Detection and Management of Diabetes : The best way to prevent diabetic retinopathy is to manage your diabetes effectively. This includes preserving appropriate levels of cholesterol, blood pressure, and blood sugar.
- Laser Surgery : Laser treatment (photocoagulation) can help seal or shrink abnormal blood vessels in the retina. It's typically used to treat proliferative diabetic retinopathy and macular edema.
- Intravitreal Injections : Medications called anti-VEGF drugs can be injected into the eye to help shrink abnormal blood vessels and reduce swelling in the retina. These injections are often used to treat diabetic macular edema.
- Vitrectomy : In advanced cases where there's bleeding into the vitreous gel in the center of the eye (vitreous hemorrhage) or traction retinal detachment, surgery called vitrectomy may be necessary. During this procedure, blood and scar tissue are removed from the eye.
- Anti-VEGF Implants : Implantable devices that release anti-VEGF medications into the eye over time are also being used to treat diabetic retinopathy.
It's essential for individuals with diabetes to maintain regular check-ups with their eye care professionals and adhere to their recommended treatment plan to prevent vision loss from diabetic retinopathy. Early detection and timely intervention are crucial in managing this condition effectively.
Types of Diabetes-related Retinopathy:
-
There are two types of diabetes-related retinopathy:
- Nonproliferative diabetes-related retinopathy (NPDR) : In this early disease stage, people have blood vessels which leak in the retina. This manifests with either fluid, hemorrhage, or lipid seen in the retina. Eventually these blood vessels close causing ischemia or poor blood flow.
- Proliferative diabetes-related retinopathy (PDR) : When the disease progresses, abnormal blood vessels grow in response to ischemia. These abnormal vessels can leak blood into the gel-like substance (vitreous) that fills your eye and cause tractional changes to the surface of the retina detaching it and resulting in severe vision loss in late stages.
Follow-up for Diabetes-related Retinopathy
It's crucial to have an eye checkup at least once a year if you have diabetes.
In the interim between eye appointments, give your doctor a call if you observe:
- Black spots in your vision.
- Blurred vision.
- Flashes of light.
- Holes in your vision.
Diabetes-related retinopathy is a danger for anybody with diabetes. This serious eye condition needs immediate treatment. Without intervention, it can lead to vision loss and even blindness. However, prompt therapy can halt the course of the illness and avoid eyesight loss. Keeping your blood sugar under control and treating your diabetes are the greatest ways to prevent the condition. Make an appointment with a medical professional if you experience any new visual abnormalities.
- Cataract Surgery & Treatment
- Multifocal Intraocular Lens (IOL)
- ICL (Implantable Collamer Lens)
- Glaucoma Surgery & Treatment
- Eye Trauma Care
- Oculoplastic, Squint, Ptosis
- Computerized Eye Testing
- Contact Lens Clinic
- Lasik Surgery
- Refractive Surgical Corrections
- Diabetic Retinopathy Screening & Treatment
- Retinal Surgery / Laser Treatment
